mechanical testing of soft tissues|elastic modulus vs soft tissue : distributor Here, we develop an instrument for high-fidelity uniaxial tensile testing of soft biological tissues in controlled environmental conditions, which is based on the closed-loop interaction between an electromagnetic actuator and .
web1 de set. de 2023 · Add the linked URL(kemono.su) to your bookmarks, in case something ever happens to this domain.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado Lotofácil 3036 – Sexta-feira – 23/02/2024. Confira .
In summary, this report demonstrates simple mechanical testing protocols to evaluate human tissues. Implementing these protocols will provide key information on the . The mechanical properties of soft tissues play a key role in studying human injuries and their mitigation strategies. While such properties are indispensable for . This report aims to provide a minimally destructive protocol to evaluate the compressive and tensile properties of human soft tissues. As examples of this technique, the . Uniaxial tensile testing is a fundamental experiment to characterize the mechanical integrity of soft connective tissues, yet a lack of test standards has hindered the .
The mechanical properties of soft tissues play a key role in studying human injuries and their mitigation strategies. While such properties are indispensable for . Here, we develop an instrument for high-fidelity uniaxial tensile testing of soft biological tissues in controlled environmental conditions, which is based on the closed-loop interaction between an electromagnetic actuator and . Recent progress includes (1) the development of tissue-compliant designs that provide minimally invasive interfaces to soft, dynamic biological surfaces and (2) . Tissue biomechanics refers to the mechanical dynamics of the human body and to the spatiotemporal variability of the intrinsic mechanical properties of biological tissues 1.Such .
Exploiting state-of-the-art three-dimensional (3D) printing, we developed a technique that not only enables the standardized clamping of soft tissues while reducing material . As examples of this technique, the tensile testing of skin and the compressive testing of cartilage are described. These protocols can also be directly applied to synthetic materials to ensure that the mechanical properties are similar to the native tissue. Protocols to assess the mechanical properties of human native tissue will allow a . Mechanical properties of soft tissues, such as stiffness, strength, and viscoelasticity (), are key to numerous biological processes (), including embryonic morphogenesis (3–5), postnatal development (), tissue .
Abstract: Reasonable constitutive models and correct material parameters are the prerequisites for effective numerical calculation and target preparation to characterize the mechanical response of biological soft tissues under high-speed impact. The typical mechanical testing methods for biological soft tissues and materials are elaborated from . The mechanical properties of soft tissues play a key role in studying human injuries and their mitigation strategies. While such properties are indispensable for computational modelling of biological systems, they serve as important references in loading and failure experiments, and also for the dev . The initial phases of tissue formation occur in extremely dynamic, active and soft environments, where three essential entities govern mechanical outcomes: volumetric growth (driven mainly by .
The mechanical behavior of soft collagenous tissues (SCT) is complex, and correspondingly, the understanding and the prediction of failure at their defects is elusive, due also to the difficulties . However, recent models have used soft tissue properties of animals for two main reasons, 1) there is a dearth of material properties representing human tissue and 2) in general, testing with animals is easier than testing with humans for material property collection [10, 11]. These challenges are compounded ever further if one wishes to obtain . The team validated the instrument by using synthetic elastomers, then used the device to examine the mechanical properties of soft tissues such as murine esophageal tissue and its constituting . The mechanical properties of biological soft tissues are inextricably linked to the field of health care, and their mechanical properties can be important indicators for diagnosing and detecting .
soft tissue properties
A method to image fiber alignment during mechanical testing of soft tissues was developed based on quantitative polarized light microscopy. Images were acquired after passing light through a rotating polarizer, a tissue sample, and an effective circular analyzer at multiple polarizer positions during uniaxial mechanical testing. The image set .Mechanical test procedures and a systematic data analysis of soft tissues are discussed with the view of providing experimental bases for the evaluation and validation of constitutive models for . Mechanical testing of any material requires adherence to proper test methods to ensure the validity and reproducibility of the measured material properties. This includes the tensile testing of musculoskeletal soft tissues that transfer tensile forces across joints, such as ligament , tendon , and meniscus . Unlike hard tissues, the soft tissues possess large deformation during the mechanical testing. In addition, soft tissues exhibit viscoelastic behavior due to the shear interaction between collagen and proteoglycan matrix. Soft tissues can be broadly divided in four categories as follows: Skin. Muscles. Connective tissues. Functional organs
Generally, techniques used to fix soft tissues for mechanical testing can be grouped into the following classifications: (i) modifying the clamp interface geometry, (ii) adding additional materials such as sandpaper or adhesive, and (iii) altering the specimen's mechanical properties in the clamped region to be more conducive to mechanical fixation.
Living tissues are active, multifunctional materials capable of generating, sensing, withstanding and responding to mechanical stress. These capabilities enable tissues to adopt complex shapes .
2. Hardware description. Since 3D printing technology is becoming more accessible and affordable, the presented preparation and clamping system does readily facilitate biomechanical testing of soft tissues thereby collecting valuable fundamental mechanical data for future medical developments. Lanir and Fung first implemented biaxial testing to measure the mechanical properties of soft tissues (rabbit skins) (Lanir and Fung, 1974). . As an alternative loading mechanism, clamps are also used in planar biaxial testing of soft tissue (Waldman and Lee, 2002). Clamps can firmly hold the edge of a material, but this method generates .
Suture method has also been employed in mechanical testing of soft tissues, typically biaxial testing. One of the reasons of using this method is some soft tissue have limited size. In addition, it is challenging to cut tissues into cruciform shape which is commonly used in testing of engineering materials. Suture allows specimen to expand . Different tissue contains different mechanical properties, therefore, different protocols should be applied in tissues with some special characterizations 45. Since there is no way to judge the .
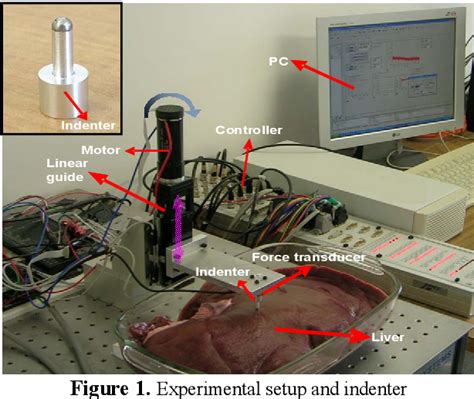
One of the most critical requirements for mechanical testing of soft biological tissues is the need to maintain them as closely to their physiological conditions (e.g., temperature, pH, osmolarity, etc.). To this aim, we designed a mounting chamber that allows immersion of the tissue test specimen in a phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) solution .
Some of the most commonly-used clamping methods for soft tissue testing affect the tissues’ mechanical properties as chemicals are involved to decelerate degradation and autolysis.
It is recommended that researchers performing soft tissue testing on solid organs make use of similar systems to provide mechanical function support to tissues tested in the laboratory setting. 5. Acknowledgements Support for this work has been provided by a grant from the US Army, under contract number DAMD 17-01-1-0677. A method to image fiber alignment during mechanical testing of soft tissues was developed based on quantitative polarized light microscopy. Images were acquired after passing light through a . Equation is the tensorial version of Eq.()The components of the tensor \(\mathbb {K}(t)\) are the different relaxation functions of the tissue, i.e. the time-dependent mechanical parameters. We will show in Sect. 2.1 that the tensor \(\mathbb {K}(t)\) can be split into its components according to a set of fourth-order bases. Thus, the resulting constitutive equation .
However, to quantify the mechanical function of the repaired or treated tissue, evaluation of the physical properties of the tissues is essential. 17–19 Unfortunately, there are a variety of mechanical tests (Fig. 1B) and widely varying protocols for each type of test. 17 This lack of standardization in testing methods and evaluation leads to . Characterizing the mechanical properties of soft biological tissues presents a formidable challenge. In order to ensure that the structure of the specimens is at a repeatable reference state, preconditioning is commonly performed before the actual test. . The spinal cord specimens were then inserted into uniaxial mechanical testing machine .
Mechanical characterisation of soft biological tissues using standard compression or tensile testing presents a significant challenge due to specimen geometrical irregularities, difficulties in .
runnig compression test
soft tissue mechanical properties
Video HOT ! HD 114. smallandcrazy Show Of Big Tits in Kitchen – Onlyfans Leaks ! HD 249. smallandcrazy/Hailey Miller Nude Topple Show Nipple – Onlyfans Leaks ! HD .
mechanical testing of soft tissues|elastic modulus vs soft tissue